Warts and moles are common skin growths that, while typically harmless, may require medical attention depending on their appearance, symptoms, or changes over time. Dermatologists evaluate these conditions to determine if treatment is necessary.
What Are Warts?
Warts are noncancerous growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear when the virus infects the top layer of skin, often through small cuts or breaks.
Types of Warts:
Common Warts: Small, rough bumps, usually on the hands or fingers.
Plantar Warts: Found on the soles of the feet; may be painful due to pressure.
Flat Warts: Smooth, flat-topped, and smaller; often appear in clusters.
Filiform Warts:Long, thin projections, usually on the face or neck.
Genital Warts: Appear in the genital area and require specialized treatment.
Treatment Options for Warts:
Cryotherapy (freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen).
Salicylic acid treatments to dissolve layers of the wart.
Electrosurgery or laser removal for stubborn warts.
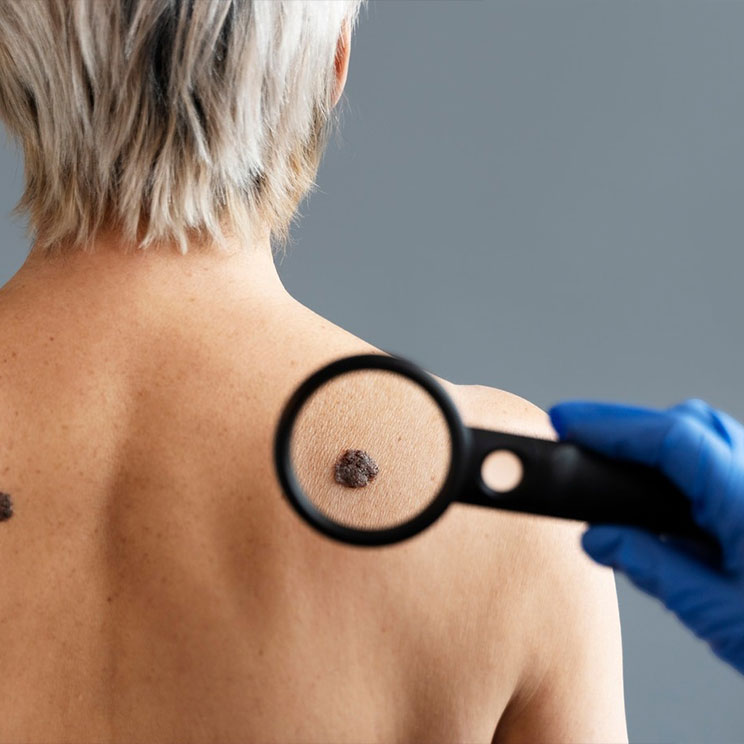
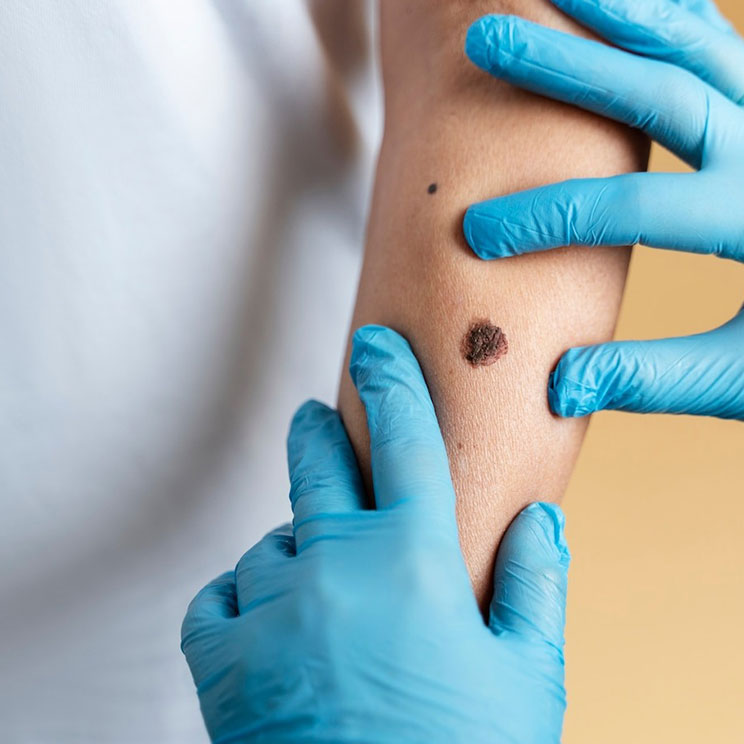
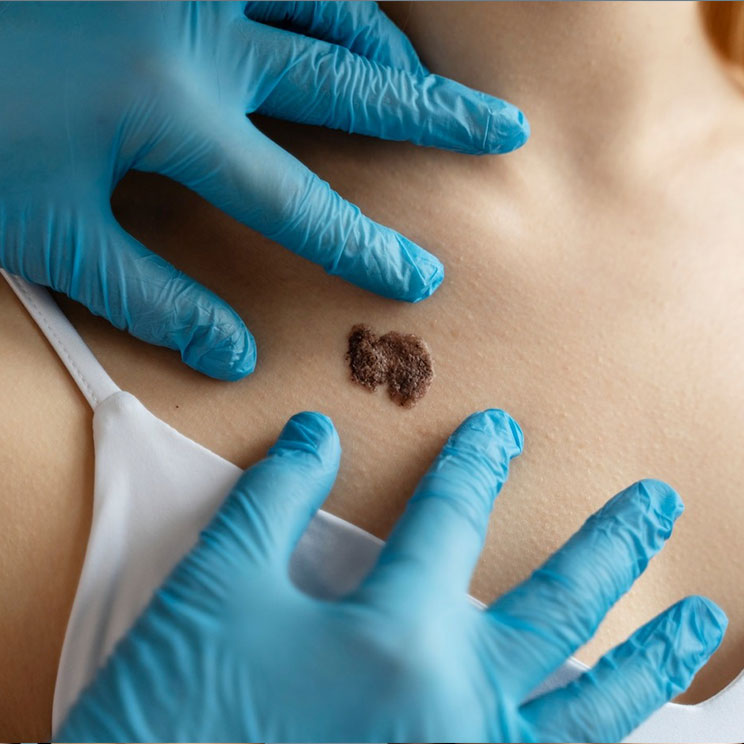
What Are Moles?
Moles, or nevi, are pigmented skin growths that develop when melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) cluster together. They vary in color, size, and shape and can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired over time.
Types of Moles:
Common Moles: Round, brown, or flesh-colored growths.
Atypical Moles: Larger or irregularly shaped moles, sometimes linked to a higher risk of melanoma.
Congenital Moles: Present at birth and may vary in size.
Treatment Options for Moles:
Observation: Monitoring for changes in size, shape, or color (ABCDE rule for melanoma
detection: Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving).
Surgical Removal: Excision or shave removal for cosmetic reasons or to rule out cancer.
When to See a Dermatologist:
Warts that are painful, spreading, or persistent despite home treatments.
Moles that itch, bleed, or show any changes in appearance.
A professional evaluation ensures proper diagnosis and personalized care for warts and moles.