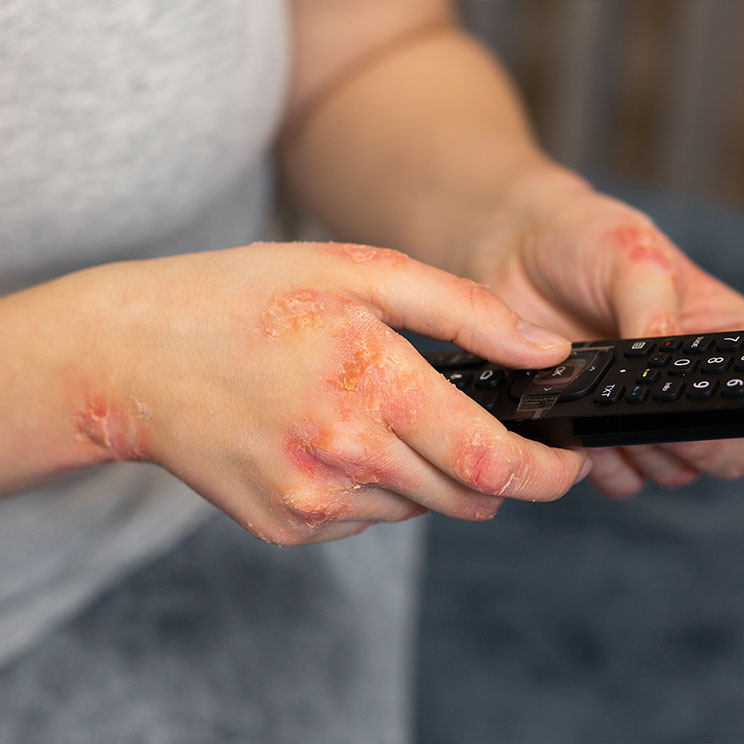
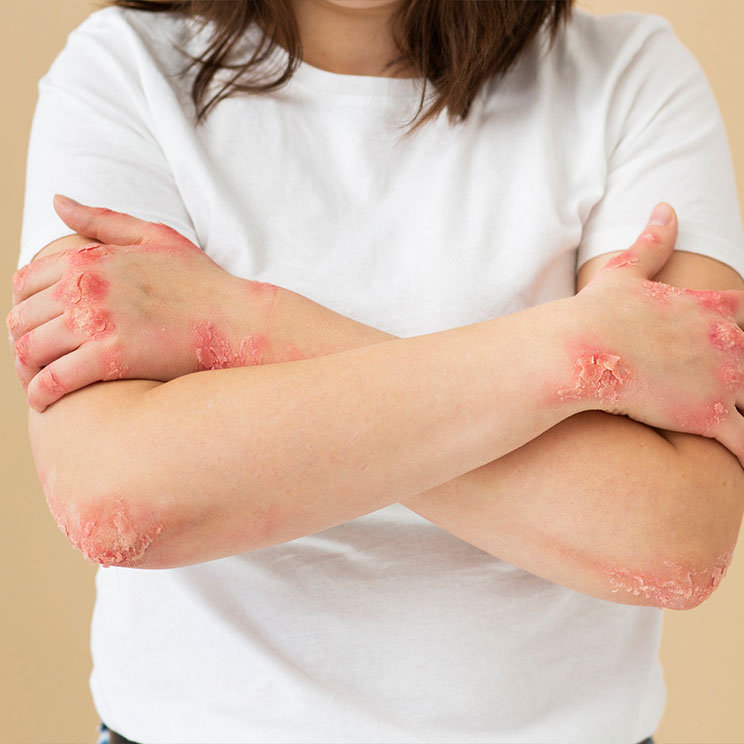
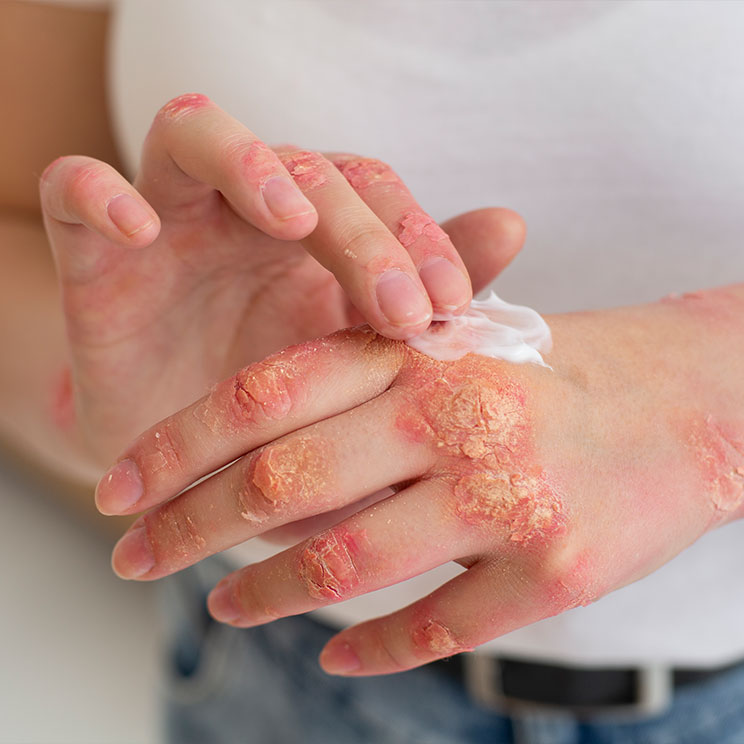
Skin infections occur when harmful microorganisms—such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites—invade the skin, causing inflammation, irritation, or other symptoms. Dermatologists classify skin infections based on the type of pathogen involved and treat them accordingly to restore skin health.
Types of Skin Infections :
1. Bacterial Infections
Examples: Impetigo, cellulitis, folliculitis.
Cause: Commonly caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria.
Symptoms Redness, swelling, pus-filled blisters, or crusted sores.
2. Viral Infections
Examples: Herpes simplex (cold sores), warts, molluscum contagiosum.
Cause: Viruses like herpesvirus or human papillomavirus (HPV).
Symptoms Blisters, sores, or wart-like growths.
3. Fungal Infections
Examples: Athlete’s foot, ringworm, candidiasis.
Cause: Fungi like Candida or dermatophytes thrive in moist areas.
Symptoms Itchy, scaly, or red patches, often in warm, damp skin folds.
4. Parasitic Infections:
Examples: Scabies, lice.
Cause: Tiny parasites burrow into or live on the skin.
Symptoms Intense itching, rashes, or visible bite marks.
5. Diagnosis and Treatment
Clinical Examination: Dermatologists assess the infection based on symptoms and appearance.
Lab Tests: Skin scrapings, cultures, or biopsies confirm the type of infection.
6.Treatment Options:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Antiviral drugs for viral conditions.
Antifungal creams or medications for fungal issues.
Topical or oral antiparasitic medications for parasitic infestations.
Preventive Measures
Maintain proper hygiene.
Avoid sharing personal items like towels.
Keep skin dry and clean to reduce fungal growth.
Use protective clothing to avoid insect bites or exposure.
Prompt treatment by a dermatologist ensures effective relief and prevents complications. Seek expert care for persistent or severe skin infections.